Toyota 4Runner: System Description
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1. GENERAL
(a) In conjunction with the impact absorbing structure for a front collision, the SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) steering pad, instrument panel passenger airbag, lower No. 1 instrument panel airbag, lower No. 2 instrument panel airbag, front seat side airbag and curtain shield airbag are designed to supplement seat belts in the event of a front collision in order to help reduce shock to the head, chest and knees of the driver and front passenger. This system is a 3-sensor type airbag system which detects the impact during a front collision using the center airbag sensor and front airbag sensors. It also operates the airbag system and seat belt pretensioners.
(b) This vehicle is equipped with electrical-type deceleration sensors for the front airbags in order to detect details about the extent of a collision during the initial stages of the collision. Therefore, the deployment of the driver airbag and instrument panel passenger airbag is controlled in two stages according to the severity of the impact.
(c) In conjunction with the impact absorbing structure for a side collision, the front seat side airbag, curtain shield airbag and front seat outer belt are designed to help reduce shock to the driver, front passenger and rear outer passengers in the event of a side collision.
(d) The curtain shield airbag helps reduce shock to the front and rear seat occupants. In conjunction with the curtain shield airbag, side airbag sensors are installed at the bottom of the front doors and rear airbag sensors are installed at the bottom of the rear pillars.
(e) In this system, a front side collision is detected by the side airbag sensor in order to simultaneously deploy the front seat side and curtain shield airbags. A rear side collision is detected by the rear airbag sensor and the center airbag sensor in order to deploy the curtain shield airbag.
(f) The center airbag sensor sends the airbag deployment signal to the ECM through the CAN (Controller Area Network) to operate the fuel pump control.
2. CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION
(a) FRONT AIRBAG SENSOR
(1) The front airbag sensors are installed on the right and left radiator supports respectively.
(2) The front airbag sensor consists of a deceleration sensor.
(3) The deceleration sensor is built into the front airbag sensor and the distortion that is created in the sensor is converted into an electric signal based on the vehicle deceleration rate during a front collision. Accordingly, the extent of the initial collision can be detected in detail.
(b) SIDE AIRBAG SENSOR
(1) The side airbag sensors are installed on the bottom of the right and left front doors respectively.
(2) The side airbag sensor consists of a deceleration sensor.
(3) The deceleration sensor is built into the side airbag sensor and the distortion that is created in the sensor is converted into an electric signal based on the vehicle deceleration rate during a front side collision. Accordingly, the extent of the initial collision can be detected in detail.
(c) REAR AIRBAG SENSOR
(1) The rear airbag sensors are installed on the right and left rear pillars respectively.
(2) The rear airbag sensor consists of a deceleration sensor.
(3) The deceleration sensor is built into the rear airbag sensor, and the distortion that is created in the sensor is converted into an electric signal based on the vehicle deceleration rate during a rear side collision. Accordingly, the extent of the initial collision can be detected in detail.
(d) REAR FLOOR SIDE AIRBAG SENSOR
(1) The rear floor side airbag sensor is installed in the center of the floor between the rear pillars.
(2) The rear floor side airbag sensor consists of a deceleration sensor.
(3) The deceleration sensor is built into the rear floor side airbag sensor and the distortion that is created in the sensor is converted into an electric signal based on the vehicle deceleration rate during a side collision. Accordingly, the extent of the initial collision can be detected in detail.
(e) CENTER AIRBAG SENSOR
(1) General
- The center airbag sensor is installed in the center floor under the instrument panel.
- The center airbag sensor consists of a deceleration sensor, safing sensor, electronic safing sensor, ignition control circuit and diagnostic circuit.
- The center airbag sensor receives signals from the deceleration sensor and safing sensor built into the center airbag sensor and front airbag sensor. Then, the center airbag sensor determines whether the steering pad, instrument panel passenger airbag, lower No. 1 instrument panel airbag, lower No. 2 instrument panel airbag, front seat side airbags and curtain shield airbags and front seat belt pretensioners should be activated, and diagnoses system malfunctions.
- The center airbag sensor causes the front seat side airbags, curtain shield airbags and front seat outer belts to deploy when receiving signals from the side airbag sensors.
- The center airbag sensor receives signals from the deceleration sensor and the electronic safing sensor built into the center airbag sensor and the rear airbag sensor, determines whether the curtain shield airbag and front seat outer belt should be activated and diagnoses system malfunctions.
- The center airbag sensor sends the airbag deployment signal to the ECM through the CAN to operate the fuel pump control.
(2) Deceleration sensor and ignition control circuit
- The deceleration sensor is built into the center airbag sensor.
- The ignition control circuit performs calculations based on the signal output from the deceleration sensors of the center airbag sensor and front airbag sensor. If the calculated values are more than the specified values, it activates an ignition operation.
(3) Safing sensor
- The safing sensor is built into the center airbag sensor. During a front collision, the sensor turns on and outputs an on signal to the center airbag sensor if a deceleration rate sent to the safing sensor is more than the specified value.
(4) Electronic safing sensor
- The electronic safing sensor is built into the center airbag sensor. During a side collision, the sensor turns on and outputs an on signal to the center airbag sensor if a deceleration rate sent to the electronic safing sensor is more than the specified value.
(5) Backup power source
- The backup power source consists of a power supply capacitor and DC-DC converter. When the power system does not function during a collision, the power supply capacitor discharges and supplies electric power to the system. The DC-DC converter operates as a boosting transformer when the battery voltage falls below a predetermined level.
(6) Diagnostic circuit
- This circuit constantly diagnoses system malfunctions. When a malfunction is detected, it turns on the SRS warning light in the combination meter to inform the driver.
(7) Memory circuit
- When a malfunction is detected in the diagnostic circuit, it is coded and stored in the memory circuit.
(f) SRS WARNING LIGHT
(1) The SRS warning light is located in the combination meter. It comes on to inform the driver of system trouble when a malfunction is detected in the self-diagnosis of the center airbag sensor. Under normal operating conditions when the ignition switch is turned to ON, it comes on for approximately 6 seconds and then goes off.
3. DEPLOYMENT CONDITION
If the vehicle is in a collision and the shock is more than the specified value, the SRS is activated automatically. The center airbag sensor includes the safing sensor and deceleration sensor. The safing sensor is designed to turn on at a lower deceleration rate than the deceleration sensor.
(a) The center airbag sensor determines whether ignition is necessary based on signals from the deceleration sensor and the front airbag sensor. If the safing sensor turns on simultaneously, current flows to the squibs to deploy the SRS as shown in the illustration below.
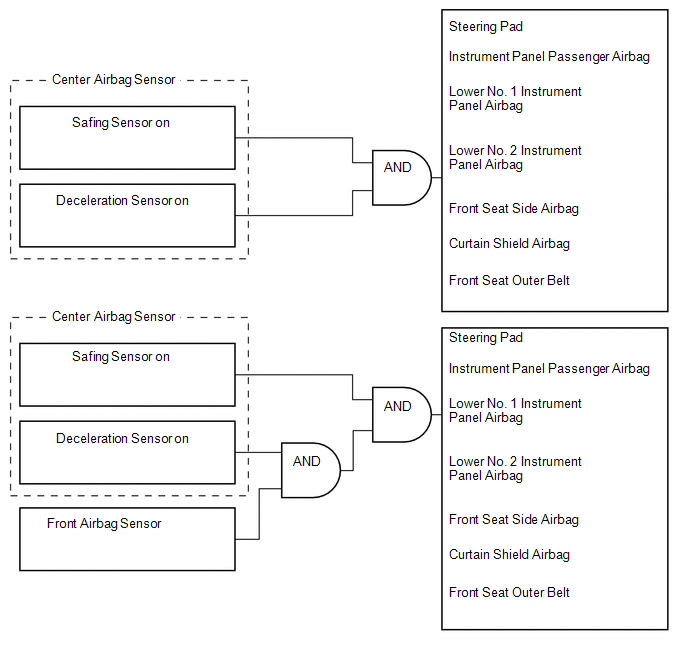
HINT:
In case of a front collision, the ignition signal may be output with the deceleration sensor on signal even without a signal from the front airbag sensor.
(b) The center airbag sensor determines whether ignition is necessary based on signals from the side airbag sensor. If the safing sensor turns on simultaneously, current flows to the squib to deploy the SRS as shown in the illustration below.
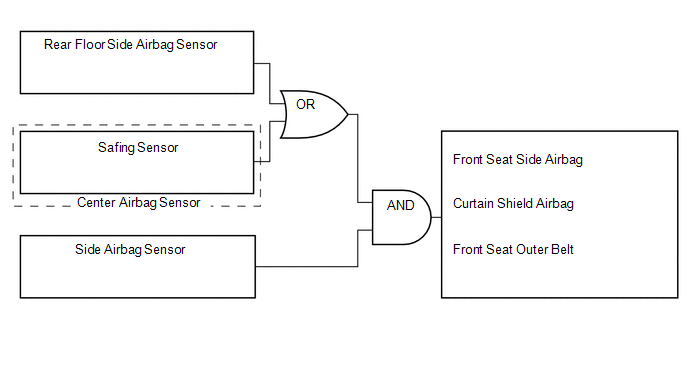
(c) The center airbag sensor determines whether ignition is necessary based on signals from the side airbag sensor and rear airbag sensor. If the safing sensor turns on simultaneously, current flows to the squib to deploy the SRS as shown in the illustration below.
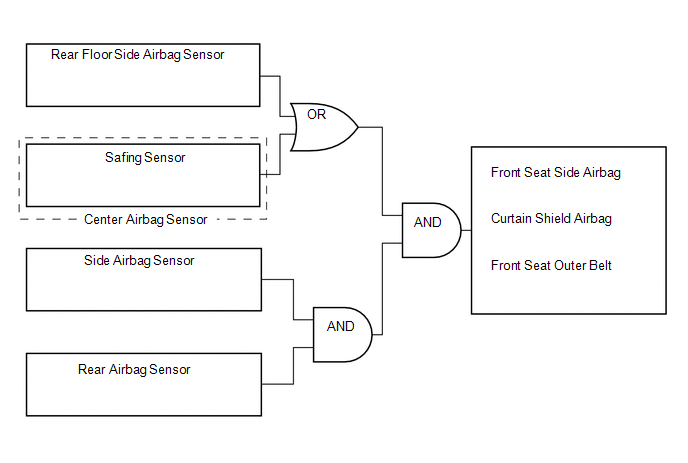
(d) The center airbag sensor determines whether ignition is necessary based on signals from the rear airbag sensor. If the safing sensor turns on simultaneously, current flows to the squib to deploy the SRS as shown in the illustration below.
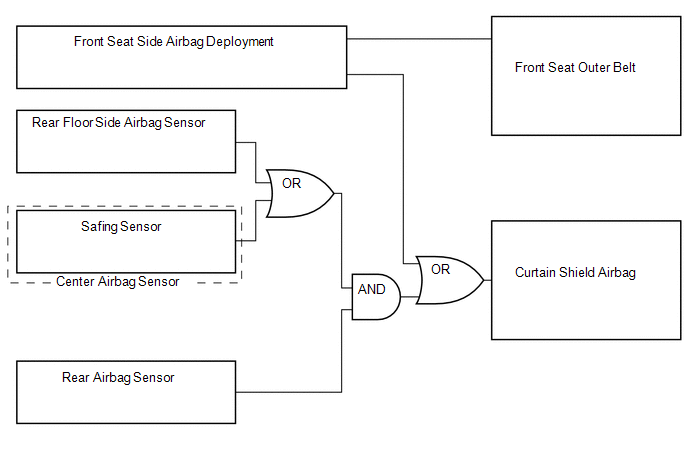
HINT:
If the front seat side airbag deploys, the curtain shield airbag will also deploy, regardless of whether the signal is output from the rear airbag sensor.
 How To Proceed With Troubleshooting
How To Proceed With Troubleshooting
CAUTION / NOTICE / HINT
HINT:
Use these procedures to troubleshoot the airbag system.
*: Use the Techstream.
PROCEDURE
1.
VEHICLE BROUGHT TO WORKSHOP
...
 Problem Symptoms Table
Problem Symptoms Table
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
HINT:
Use the table below to help determine the cause of problem symptoms. If multiple
suspected areas are listed, the potential causes of the symptoms are listed in order
...
Other materials about Toyota 4Runner:
Open in Outside Luggage Compartment Electrical Key Antenna Circuit (B27A8)
DESCRIPTION
The certification ECU generates a request signal and transmits the signal to
the electrical key antenna (outside luggage). The electrical key antenna (outside
luggage) detects that the electrical key is brought close to the vehicle, and when
...
Operation Check
OPERATION CHECK
NOTICE:
Perform initialization before performing the operation check.
1. CHECK AUTO OPERATION
HINT:
When pressing the switch for 0.3 seconds or less, the roof glass moves but auto
operation does not operate.
(a) Turn the ignition switch ...
0.0246
